
Biblical Biology – Life’s Origins
In 1859, something remarkable was about to happen.
For thousands of years, people had believed that life could condense out of non-living matter. This, of course, was why maggots appeared out of rotting meat, and why fleas appeared from dust – or so it was thought.
While experiments by scientists like Francesco Redi had long ago proven that complex organisms like maggots and fleas did not arise from non-living matter, the question was still unanswered for simpler forms of life. Microbes (like bacteria), for instance, were thought to emerge spontaneously from water or broth.
It was an idea that would soon be challenged.
Biogenesis – Nature’s Law
In 1859, the now famous scientist Louis Pasteur ran a unique experiment.
In it, he boiled broth in a swan-necked flask. Boiling the liquid killed off any bacteria present inside the liquid, while the swan-necked opening prevented new bacteria from falling in out of the air.
Contrary to the predictions of spontaneous generation, the broth did not become cloudy with newly created microorganisms, but remained clear. Only after the swan neck was removed (allowing contaminants into the flask) did the broth cloud.
This established an important point that remains foundational to the study of biology today. It is called the law of biogenesis:
[feature_box style=”10″ only_advanced=”There%20are%20no%20title%20options%20for%20the%20choosen%20style” alignment=”center”]
The Law of Biogenesis – Living things only come from other living things.
[/feature_box]
The Search for First Life
The law of biogenesis states that life only comes from pre-existing life. To this day, it stands with no known exceptions.
But where did the first life come from?
Despite Pasteur’s historic experiment, spontaneous generation remains the most popular theory among secular scientists today, with many research dollars being spent trying to find a way around Pasteur’s law of biogenesis.
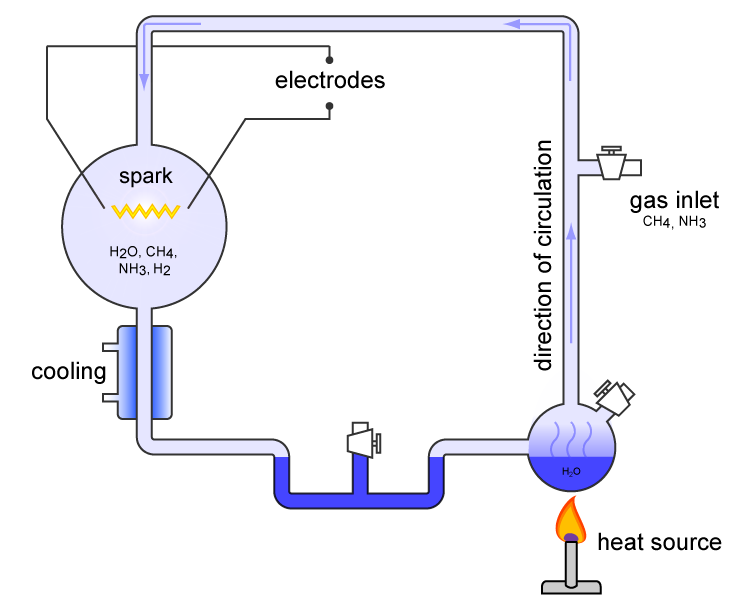
The most famous of these attempts was an experiment preformed by Stanley Miller in 1952.
In this experiment, methane, ammonia, and hydrogen were sealed inside a glass flask, partly filled with liquid water (the intent being to simulate the environment of the early Earth). These chemicals were then subjected to electrical sparks (“lightning”) and allowed to react with one another.
Today, the Miller-Urey experiment, as it is called, is hailed as a triumph of secular science, having successfully produced amino acids, one of the building blocks of life, from simple chemical reactions.
Certainly, it was a victory for spontaneous generation – or was it?
A Second Look at Miller-Urey
Unfortunately, the truth of the experiment’s results are far less encouraging than the stories would have you believe.
Not only did the Miller-Urey experiment only produce a very small amount of amino acids (half of which were the wrong kind anyway), it also produced a lot of other things, most of which were actually toxic to the formation of life. Jerry Bergman explains:
The Miller–Urey experiments produced many other compounds aside from amino acids, resulting in a sticky mass that was actually further from the building blocks of life than were the postulated original precursor chemicals. Toxic compounds produced include cyanides, carbon monoxide, and others—actually most of the dark matter in the solution could not be identified by the researchers in 1953.1)Bergman, Jerry. “Why the Miller-Urey research argues against abiogenesis.” Journal of Creation 18, no. 2 (August 2004): 28-36.
The biggest mistake in all of the hype surrounding this experiment though, is the way its supporters liken it to “creating life in the laboratory,” as though creating life is simply a matter of getting the right chemicals together.
This oversimplifies the problem. The building blocks of life come together all the time without creating new organisms (the meat sitting in your freezer is a good, if morbid example of this).
Clearly, there is more to life than mere chemicals.
Design and the Information Problem
Consider a snowflake – it is a highly ordered, yet highly complex structure, appearing in a dazzling array of patterns.
In some ways, the snowflake appears to be hand-crafted, but it is not. Alex Williams explains:
When water freezes, its crystals take the form of a hexagonal prism. Crystals then grow by joining prism to prism. The elaborate branching patterns of snowflakes arise from the statistical fact that a molecule of water vapour in the air is most likely to join up to its nearest surface. Any protruding bump will thus tend to grow more quickly than the surrounding crystal area because it will be the nearest surface to the most vapour molecules. There are six ‘bumps’ (corners) on a hexagonal prism, so growth will occur most rapidly from these, producing the observed six-armed pattern.2)Williams, Alex. “Life’s irreducible structure – Part 1: autopoiesis.” Journal of Creation 21, no. 2 (August 2007): 110.
The structure of the snowflake, though elaborate, can be traced back to the simple, predictable behavior of water molecules. As a result, knowing the rules of this behavior, one might predict the possibility of snowflakes without ever having seen one.
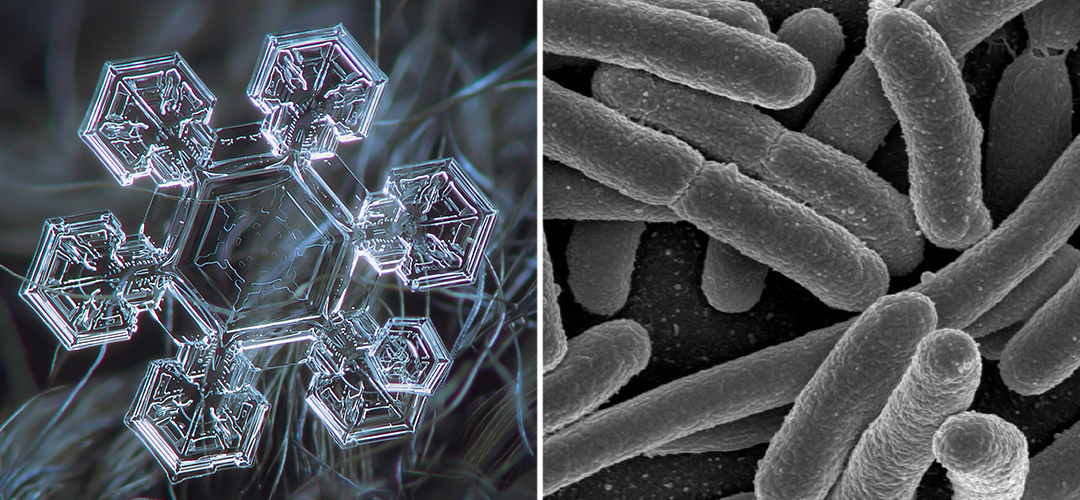
The organized complexity of the snowflake (left – Source) is a natural extension of how water molecules behave in cold temperatures. The same cannot be said for living things, like these E. coli (right), whose molecular components do not naturally form cellular structures.
Cells, the basic units of life, are also highly ordered and complex, yet, unlike the snowflake, their structure occurs not because of, but in spite of the natural behavior of their components.
It is no secret in biology that the building blocks of life are highly unstable. Our DNA, for example, suffers millions of damaging mutations every day (many from its own internal chemistry). Were it not for sophisticated repair mechanisms (ironically programmed by the DNA itself), the DNA strand would completely destroy itself in a short period of time.
This pattern of instability carries across most of the biological world and is one reason why our bodies must feed and repair themselves. It is also the reason that living things die.
The process of death has been described as “the victory of chemistry over biology,” but if the laws of mass action chemistry are so hostile to the specified order of life, how can they have created that order in the first place?
It is clear that the structure of life must have been imposed by an outside force.
The Logic of Design
But is all of this discussion of “intelligent designers” simply explaining away difficult scientific problems? Isn’t it just a matter of time before science eventually finds the answer?
What is often misunderstood is the fact that intelligent design is not an argument from ignorance (“we don’t know how ‘x’ could have formed naturally, therefore it must be designed”), but an argument from inference (“we know that ‘x’ shares qualities seen only in designed things, therefore it was probably designed”).
Living systems are teeming with information. Rough estimates suggest that the average human cell contains about 3 gigabytes of information in its DNA (about 1,000 terabytes per cubic meter)3)Sarfati, Jonathan. “DNA Best Information Storage – Creation.com.” Creation | Creation Ministries International. Last modified October 9, 2015. http://creation.com/dna-best-information-storage. We know from observation that information can be conserved and destroyed, but there is no known natural process by which information can be created.
The creation of information is only ever observed when nature is acted upon by an intelligent source. Why should the information of life be an exception?
Conclusion
In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth.
Genesis 1:1
The first and most foundational principle in biblical biology is that God, not chemistry, created life.
This idea is supported by the observations that life only comes from pre-existing life, that life’s specified complexity exists in spite of its chemical parts, not because of them, and that life is teeming with information, which has only ever been shown to originate from intelligent sources.
From these lines of evidence, it becomes clear that design is not only good theology, it’s good science as well.
References
| ↑1 | Bergman, Jerry. “Why the Miller-Urey research argues against abiogenesis.” Journal of Creation 18, no. 2 (August 2004): 28-36. |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | Williams, Alex. “Life’s irreducible structure – Part 1: autopoiesis.” Journal of Creation 21, no. 2 (August 2007): 110. |
| ↑3 | Sarfati, Jonathan. “DNA Best Information Storage – Creation.com.” Creation | Creation Ministries International. Last modified October 9, 2015. http://creation.com/dna-best-information-storage. |

Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.